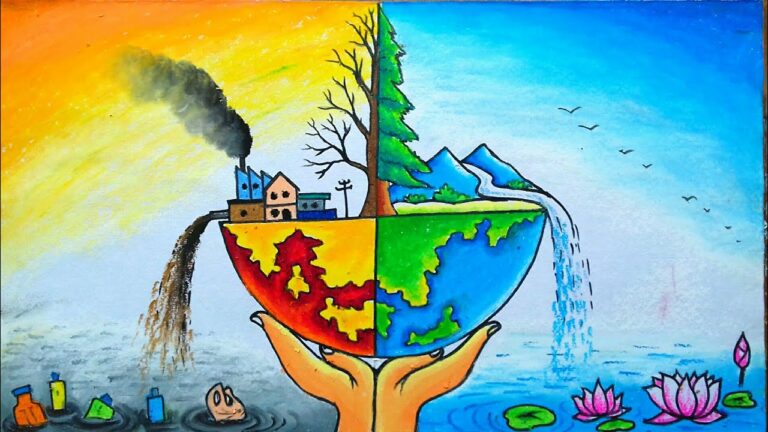
There Is a Big Difference Between Good and Bad Environment, And That Difference Matters a Lot.
Environment is the surroundings in which living and non-living things live, interact, grow and perish.
The term Environment is derived from French terms ‘virer (to turn) or ‘in/viron’ meaning to encircle; and denotes the interaction between natural surroundings and organisms including human beings.
Environment: Four Components of Environment

The four major components of environment corresponding to rocks, water, air and life include:
- Lithosphere is the outermost layer of earth called crust, which is made of different minerals. Its depth can reach up to 100 kilometers and is found on both land (terrestrial crust) and oceans (oceanic crust). The main component of lithosphere is earth’s tectonic plates.
- Hydrosphere comprises of all forms of water bodies on earth including oceans, seas, rivers, lakes, ponds, streams etc. It covers 70% of earth’s surface. 97.5% of water found on Earth is in the oceans in the form of salt water. Only 2.5 % of water on Earth is freshwater. Out of this, 30.8% is available as groundwater and 68.9% is in frozen forms as in glaciers. Amount of 0.3% is available in rivers, reservoirs and lakes and is easily accessible to man.
- Atmosphere is gaseous layer enveloping the Earth. The atmosphere with oxygen in abundance is unique to Earth and sustains life. It mainly comprises 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.038% carbon dioxide, and traces of hydrogen, helium, and noble gases. The amount of water vapour present is variable.
- Biosphere refers to all the regions on Earth where life exists. The ecosystems that support life could be in soil, air, water or land. The term Biosphere was coined by Geologist Edward Suess who used this term for place on Earth where life can be found. Biosphere refers to the sum total of all living matter, the biomass or biota. It extends from the polar ice caps to the equator, with each region harboring some life form suitable to the conditions there.
Environmental problems should be controlled by

- Pollution Control
- Tree plantation drives
- No Plastic Initiatives – “Say No to Plastics “
- Rain water Harvesting
POLLUTION CONTROL
Pollution control is the process of reducing or eliminating the release of pollutants into the environment. It is regulated by various environmental agencies which establish pollutant discharge limits inform of air, water, and land.
Pollution management deals with pollutants control from air, water, soil and waste management system
TREE PLANTATION
Tree Plantation plays a major role in maintaining the environmental ecological balance by Reducing the Climate Change, Purifying Air, provides Natural Air Conditioning, Saves Water, Prevents Water Pollution and Provides Shelters for Wildlife
SAY NO TO PLASTICS
The world is facing a global plastics crisis. Out of the 8.3 billion tons of plastics produced since the 1950s, 79% ended in landfills or leaked into the environment.
Plastic pollution is a rather new but exponentially growing phenomenon. Annual global plastic production has exploded over the past decades, going from some 1.5 million metric tons (MT) in 1950 to an astonishing 368 million MT in 2019. Plastic production is expected to further increase in the coming decades as current investments in petrochemical infrastructure support this trend. Under business-as-usual scenarios, annual production could reach up to 2’000m MT by 2050.
The ongoing boom of plastic production is tightly linked to its reliance on fossil fuels, and major investments in petrochemical infrastructures in key regions of the world. While 99% of plastic materials are produced from fossil feedstock, these industries are closely connected.
RAIN WATER HEARVESTING
Rainwater harvesting is the simple process or technology used to conserve rainwater by collecting, storing, conveying and purifying of rainwater that runs off from rooftops, parks, roads, open grounds, etc. for later use.
The rainwater harvesting system is one of the best methods practised and followed to support the conservation of water. Today, scarcity of good quality water has become a significant cause of concern. However, rainwater, which is pure and of good quality, can be used for irrigation, washing, cleaning, bathing, cooking and also for other livestock requirements.
The benefits of the rainwater harvesting system are Less cost, Helps in reducing the water bill,
Decreases the demand for water, Reduces the need for imported water, Promotes both water and energy conservation, Improves the quality and quantity of groundwater, Does not require a filtration system for landscape irrigation. This technology is relatively simple, easy to install and operate.
It reduces soil erosion, stormwater runoff, flooding, and pollution of surface water with fertilizers, pesticides, metals and other sediments.
It is an excellent source of water for landscape irrigation with no chemicals, dissolved salts and free from all minerals.